- GD&T
GENERAL DIMENSIONING- International Paper Size Standards
- Technical Drawing Styles
- ISO And ANSI Projections
- ANSI Technical Drawing Views
- Technical Drawing Dimesioning Types
- ANSI and ISO Geometric Tolerancing Symbols
- Geometric Tolerancing Reading
- Taylor Principle Rule#1
- Form Tolerances
- Profile Tolerances
- Orientation Tolerances
- Location Tolerances
- Runout Tolerances
- TOLERANCES
ANSI AND ISO- Tolerancing and Engineering Standards
- Hole and Shaft Basis Limits And Fits
- ISO International System For Limits And Fits
- International Tolerance Grade (IT)
- Fundamental Deviations For Hole and Shaft Basis
- ISO Tolerance Band IT01-IT16
- Calculation Of International Tolerance
- Calculation of Upper and Lower Deviation For Shaft
- Calculation of Upper and Lower Deviation For Holes
- ISO Shaft Tolerances (3mm-400mm)
- ISO Shaft Tolerances (400mm-3150mm)
- ISO Hole Tolerances (3mm-400mm)
- ISO Hole Tolerances (400mm-3150mm)
- ANSI Standard Limits and Fits
- METAL CUTTING TECHNOLOGIES
- Terms and Definitions of the Cutting Tools
- Cutting Tool Materials
- Selection of Carbide to machine the work-part
- Identification System For Indexable Inserts
- Work-Part Materials
- Machinability and the specific cutting force
- Machinability of the Certain Material Evaluations
- Cutting Forces and Chip Formations
Machinability and The Specific Cutting Force for Work-piece Materials
The condition and physical properties of the work material have a direct influence on the machinability of a work material. The various conditions and characteristics described as "condition of work material," individually and in combinations. Dividing the materials into 6 groups does not provide enough information to select the correct cutting tool geometry, grade and cutting data. There are many different metals commercially available. Some are easier to machine than others. Many years ago, a system was developed to rate the relative ease or difficulty of machining various metals. These ratings are called “Machinability Ratings.” Machinists and manufacturing engineers use machinability ratings when they select tool material, feed rates, and machine speeds for metal cutting and grinding operations. The material groups have to be broken down further into sub-groups, etc. In order to be even more specific in work-piece material will assist the user in improving productivity. It means “the ease with which a given material may be worked with a cutting tool.” The cutting process is impacted by variables like cutting speed, dimensions of the cut, tool form, tool material, the cutting fluid, rigidity of tool holding device, and the level of tool/part impact relative to constant or intermittent contact. However, the machinability rating provides a starting point for understanding the severity of a metalworking operation.
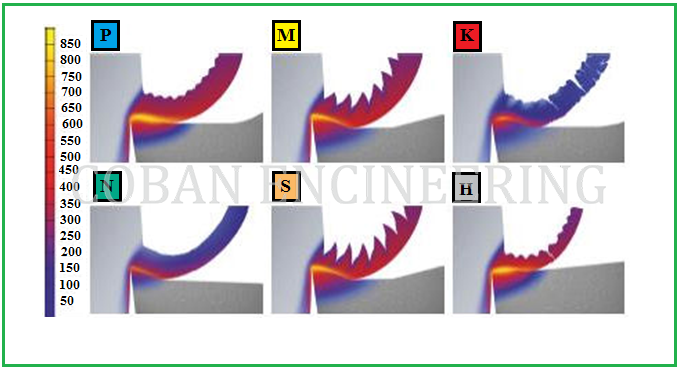
Machinability can be difficult to predict because machining has so many variables. Machinability has no direct definition, like grades or numbers. In a broad sense it includes the ability of the work-piece material to be machined, the wear it creates on the cutting edge and the chip formation that can be obtained. Two sets of factors are the condition of work-piece materials and the physical properties of work-piece materials. The condition of the work-piece material includes eight factors: microstructure, grain size, heat treatment, chemical composition, fabrication, hardness, yield strength, and tensile strength. Physical properties are those of the individual material groups, such as the modulus of elasticity, thermal conductivity, thermal expansion, and work hardening etc.
AISI (The American Iron and Steel Institute) tested many alloys and compared the normal cutting speed, tool life and surface finish to that obtained when machining B1112. Machinability ratings are “relative” ratings. They compare the ease of machining an alloy to a standard. That standard is 160 Brinell hardness B1112 cold drawn steel machined at 180 surface feet per minute. B1112 was assigned a score of 1.00. The machinability of all other alloys is compared to the standard score of 1.00. Materials with scores above 1.00 are easier to machine than B1112. Likewise, materials with scores of less than 1.00 are more difficult to machine. For example, Inconel is an alloy that is very difficult to machine and it has a rating of 0.09.
Work-pieces material's chemistry have important effects on work-piece material properties. In some cases chemistry affects the wear mechanisms that act in the cutting tool material. Through these relationships, work-piece material chemistry affects machinability of the work-piece. Carbon content has a significant effect on the properties of the steel. If carbon level is increased in work-piece material, the strength and the hardness of the steel will increase. This reduces machining performance of the work-piece. Many alloying elements added to steel to enhance properties of the work-piece are detrimental to machinability. Molybdenum, Chromium, and Tungsten from carbides in steel, which increase tool wear and reduce machinability. Nikel and Manganese add strength and toughness to steel, which reduce machinability. Certain elements can be added to steel to improve machining performance, Such as Lead, Sulfur, Phosphorus etc. The additives have effect of reducing the coefficient of the friction. Better tool life and surface finish result from these effects. Machinability Rating chart based on AISI shown below;
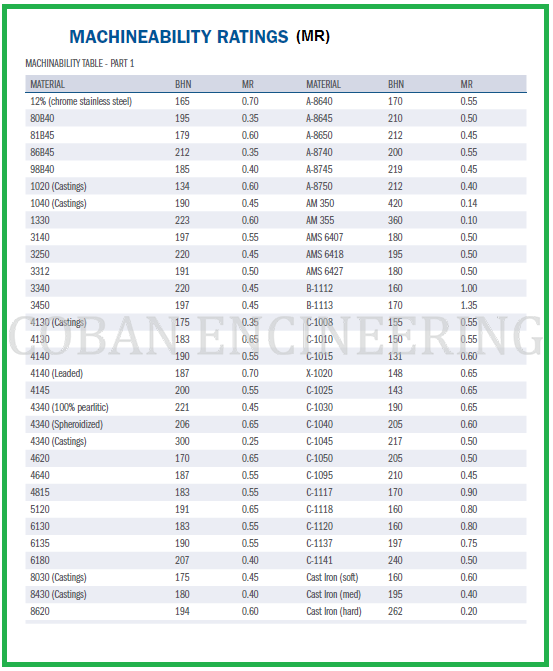
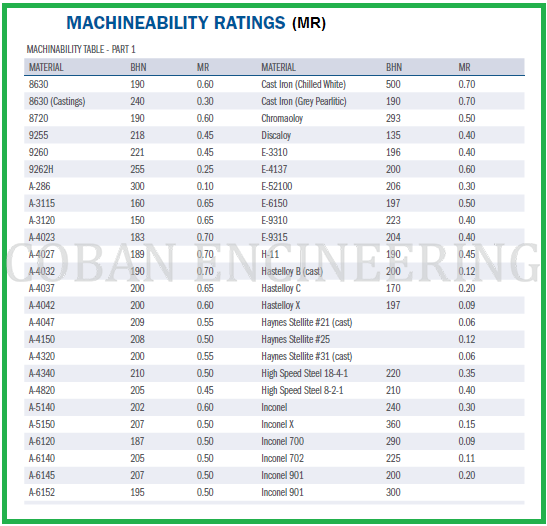
Copyright ©2010-2023 Coban Engineering.All Rights Reserved.