- GD&T
GENERAL DIMENSIONING- International Paper Size Standards
- Technical Drawing Styles
- ISO And ANSI Projections
- ANSI Technical Drawing Views
- Technical Drawing Dimesioning Types
- ANSI and ISO Geometric Tolerancing Symbols
- Geometric Tolerancing Reading
- Taylor Principle Rule#1
- Form Tolerances
- Profile Tolerances
- Orientation Tolerances
- Location Tolerances
- Runout Tolerances
- TOLERANCES
ANSI AND ISO- Tolerancing and Engineering Standards
- Hole and Shaft Basis Limits And Fits
- ISO International System For Limits And Fits
- International Tolerance Grade (IT)
- Fundamental Deviations For Hole and Shaft Basis
- ISO Tolerance Band IT01-IT16
- Calculation Of International Tolerance
- Calculation of Upper and Lower Deviation For Shaft
- Calculation of Upper and Lower Deviation For Holes
- ISO Shaft Tolerances (3mm-400mm)
- ISO Shaft Tolerances (400mm-3150mm)
- ISO Hole Tolerances (3mm-400mm)
- ISO Hole Tolerances (400mm-3150mm)
- ANSI Standard Limits and Fits
- METAL CUTTING TECHNOLOGIES
- Terms and Definitions of the Cutting Tools
- Cutting Tool Materials
- Selection of Carbide to machine the work-part
- Identification System For Indexable Inserts
- Work-Part Materials
- Machinability and the specific cutting force
- Machinability of the Certain Material Evaluations
- Cutting Forces and Chip Formations
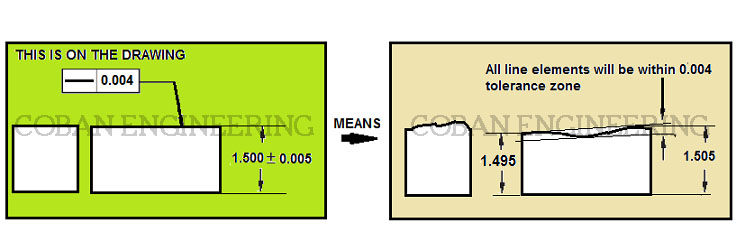
Straightness on the flat surface shown below;
Flatness:
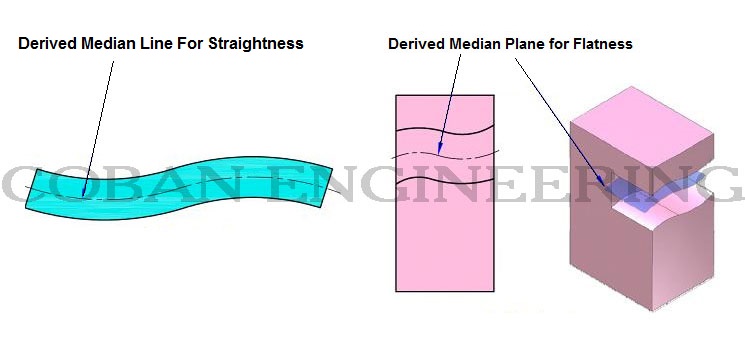
Flatness is a condition of a specified surface having all elements in one plane. Flatness tolerance provides a tolerance zone of specified and defined by two parallel planes in where the specified surface must lie. Flatness is applied to an individual surface, flatness tolerance does not need to be related to a datum. A feature control frame is attached to the surface with a leader or extension line. When a feature control frame with a flatness tolerance is applied with a size dimension, the flatness tolerance applies to the median plane for a noncylindrical surfaces. The derived median plane is composed of the midpoint of the actual local size. The median plane is not necessarily flat. The flatness tolerance may be used to control the form of derived median plane. Also the straightness tolerance may be used to control the form of the derived line.
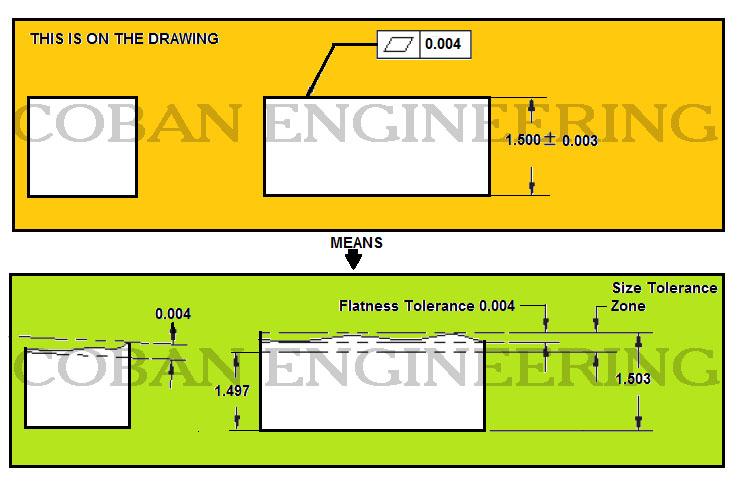
The Surface must lie between two planes 0.004 apart from each other and the specified surface must be within the specified limit of size tolerance.
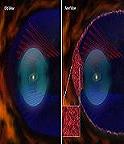
Circularity:
Circularity is a condition of a surface of a part. Circularity tolerance is used to control the roundness of circular parts or features. Circular features can be defined by cylinders, spheres, and cones. Circularity tolerance controls each circular element of a cylinder independent of each other. Circularity tolerance is applied to an individual surface, Circularity tolerance does not need to be related to a DATUM. The Circularity tolerance of the manufacturing part specifies where all points of a surface of a circular part must lie in the zone bounded by two concentric circles which radiis differ by the tolerance value of the concentricity.
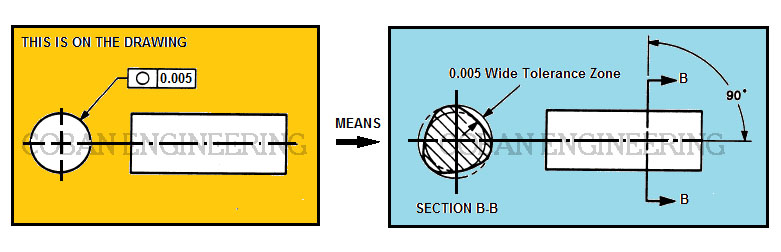
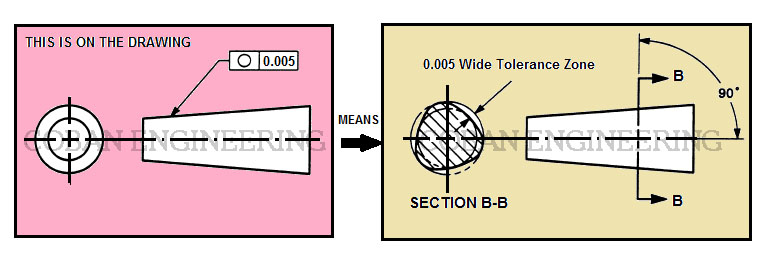
Specified surface must be processed with the specified tolerance zone within 0.005
Copyright ©2010-2023 Coban Engineering.All Rights Reserved.